Blood test
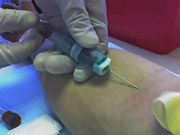
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a needle, or via fingerprick.
Blood tests are used to determine physiological and biochemical states, such as disease, mineral content, drug effectiveness, and organ function. They are also used in drug tests. Although the term blood test is used, most routine tests (except for most haematology) are done on plasma or serum, instead of blood cells.
Contents |
Extraction
Venipuncture is useful as it is a relatively non-invasive way to obtain cells and extracellular fluid (plasma) from the body for analysis. Since blood flows throughout the body, acting as a medium for providing oxygen and nutrients, and drawing waste products back to the excretory systems for disposal, the state of the bloodstream affects, or is affected by, many medical conditions. For these reasons, blood tests are the most commonly performed medical tests.
Phlebotomists, laboratory technicians and nurses are those charged with patient blood extraction. However, in special circumstances, and emergency situations, paramedics and physicians sometimes extract blood. Also, respiratory therapists are trained to extract arterial blood[1][2] for arterial blood gases.
Types of blood tests
Biochemical analysis
A basic metabolic panel measures sodium, potassium, chloride, bicarbonate, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), magnesium, creatinine, and glucose. It also sometimes includes calcium.
Some blood tests, such as those that measure glucose, cholesterol, or for determining the existence or lack of STD, require fasting (or no food consumption) eight to twelve hours prior to the drawing of the blood sample.
For the majority of blood tests, blood is usually obtained from the patient's vein. However, other specialized blood tests, such as the Arterial blood gas, require blood extracted from an artery. Blood gas analysis of arterial blood is primarily used to monitor carbon dioxide and oxygen levels related to pulmonary function, but it is also used to measure blood pH and bicarbonate levels for certain metabolic conditions.
While the regular glucose test is taken at a certain point in time, the glucose tolerance test involves repeated testing to determine the rate at which glucose is processed by the body.
Normal ranges
| Test[3] | Low | High | Unit | Comments |
| Sodium (Na) | 136 | 145 | mmol/L | |
| Potassium (K) | 3.5 | 5.5 | mmol/L | |
| Urea | 2.5 | 6.4 | mmol/L | BUN - blood urea nitrogen |
| Urea | 7 | 18 | mg/dL | |
| Creatinine - male | 62 | 115 | μmol/L | |
| Creatinine - female | 53 | 97 | μmol/L | |
| Creatinine - male | 0.7 | 1.3 | mg/dL | |
| Creatinine - female | 0.6 | 1.1 | mg/dL | |
| Glucose (fasting) | 3.9 | 5.8 | mmol/L | See also glycosylated hemoglobin |
| Glucose (fasting) | 70 | 105 | mg/dL |
Molecular profiles
- Protein electrophoresis (general technique -- not a specific test)
- Western blot (general technique -- not a specific test)
- Liver function tests
- Polymerase chain reaction (DNA). DNA testing is today possible with even very small quantities of blood: this is commonly used in forensic science, but is now also part of the diagnostic process of many disorders.
- Northern blot (RNA)
- Sexually transmitted diseases
Cellular evaluation
- Full blood count (or "complete blood count")
- Hematocrit and MCV ("mean corpuscular volume")
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- Cross-matching. Determination of blood type for blood transfusion or transplants
- Blood cultures are commonly taken if infection is suspected. Positive cultures and resulting sensitivity results are often useful in guiding medical treatment.
Future alternatives
In 2008, scientists announced that the more cost effective saliva tests could eventually replace some blood tests, as saliva contains 20% of the proteins found in blood. [4]
See also
- Reference ranges for common blood tests (with a much longer list)
- Urine test, another common style of body fluid test
- Schumm test, a common test for blood mismatch
- Blood film, a way to look at blood cells under a microscope
- Hematology, the study of blood
References
- ↑ Aaron SD, Vandemheen KL, Naftel SA, Lewis MJ, Rodger MA (2003). "Topical tetracaine prior to arterial puncture: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial". Respir Med. 97 (11): 1195–1199. doi:10.1016/S0954-6111(03)00226-9. PMID 14635973.
- ↑ http://www.michigan.gov/careers/0,1607,7-170-46398-64537--,00.html
- ↑ C. A. Burtis and E. R. Ashwood, Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry (1994) 2nd edition, ISBN 0-7216-4472-4
- ↑ Press TV - Saliva test to substitute blood test
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||